The Hot and Cold of it
Posted on November 12th, 2019 by Andries Lodder
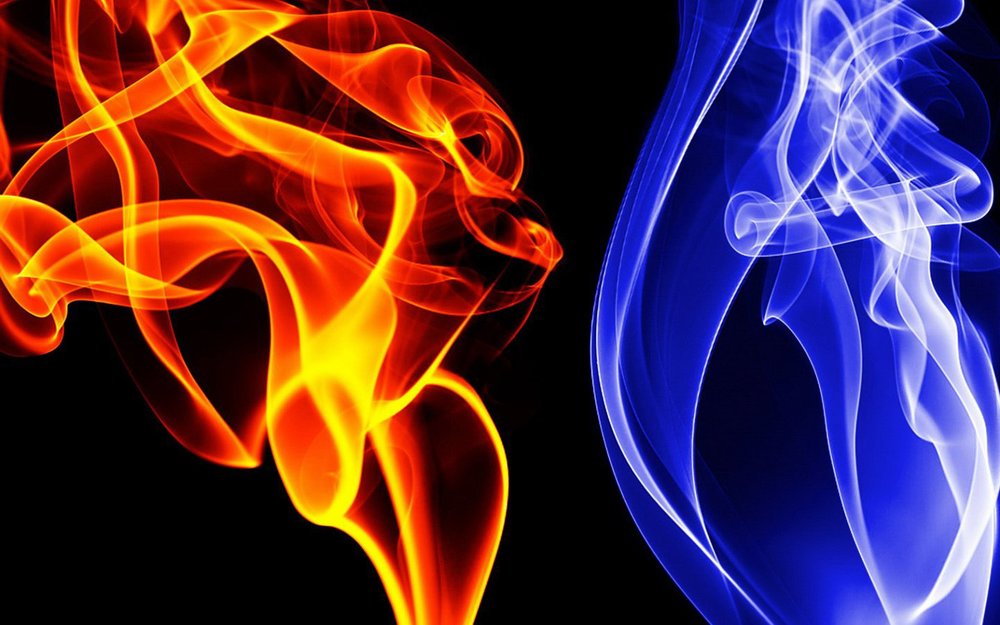

Ice and heat as recovery techniques:
All elite athletes know that it’s not only what you do in training that matters. In fact, those hours before and after training are just as important as the hours in the gym or on the field.
It is in these hours that using various recovery techniques come into play. Recovery can be a number of things, from the nutrition you eat before and after training, the sleep you get at night as well as using modalities such as heat, ice, compression or muscle stimulation that you use, that can help the body heal and recover in time for the next training session.
Using heat and ice can be very beneficial to your recovery. However, what is the actual science behind these difference techniques?
Heat Therapy:

The key to heat therapy is blood flow. When heat is applied to an area of the body, the body naturally sends more blood to the area. With an increase in blood flow there come an increase in oxygen and nutrients as well as an increase in the removal of waste products. All of this assists in the normal functioning of a muscle and in the healing of a muscle after being placed under stress. Heat therapy is also very beneficial in reducing pain as well as tension in muscle groups.
Heat can be specifically beneficial in helping with injuries, apply a heat pack for 10-15 minutes before or after training in order to help keep muscles fresh and recovered.
Ice Therapy:

In contrast to heat therapy, applying ice or cold to an area decreases the amount of blood flow. This may seem like a bad thing as blood flow is so good for healing but in fact it can be very beneficial. By slowing down blood flow to an area it will decrease the risk of injury, spasms, cramps and inflammation. By decreasing swelling, pain and inflammation it assists in allowing your muscles to function at a 100% come game time. Cold therapy can be applied in a number of ways, from ice packs and ice baths to cryotherapy and freezing chambers. It is best to apply cold after exercise and not before.
Combing the use of hot and cold therapies can be very beneficial to performance. It is advised to apply the cold first and then the heat, each for roughly 10-15 minutes. This will allow for optimal results but won’t cause any negative side effects. Never apply the heat or cold directly to the skin and don’t leave it on for more then 20 minutes as it can cause lasting nerve damage to the area.
For more information on recovery techniques give us a call and we can tell you what’s best for you!