Understanding Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Posted on September 30th, 2024 by Andries Lodder
Shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS) poses a significant challenge for athletes engaged in overhead sports. The intricate mechanics of the shoulder joint, combined with the repetitive stress of overhead movements, makes this condition prevalent among athletes. This Article delves into the different types of shoulder impingement, diagnostic approaches, and current management strategies to help athletes and healthcare professionals navigate this complex issue.
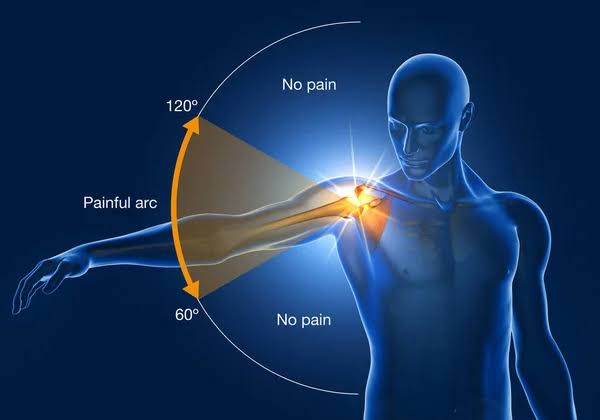
Types of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
- Subcoracoid Impingement Subcoracoid impingement involves the compression of the anterior soft tissues of the shoulde. This is between the coracoid process and the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. This type of impingement can lead to significant discomfort and functional limitations, particularly in sports that involve repetitive forward motions.
- Subacromial Impingement Syndrome (SIS) Subacromial impingement occurs due to the extrinsic compression of the rotator cuff tendons. Generall, between the humeral head and the coracoacromial structures. It can also result from intrinsic degeneration of the supraspinatus tendon, which causes superior migration of the humeral head. This condition is frequently observed in athletes who engage in repetitive overhead activities, such as baseball pitchers or swimmers.
- Internal Impingement Internal impingement is a prevalent cause of shoulder pain in overhead athletes. It arises from the repetitive impingement of the articular surface. Generally during extreme abduction and external rotation of the arm. This type of impingement is particularly common among athletes performing high-intensity overhead motions.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosing shoulder impingement syndrome involves a thorough assessment that includes:
- Sport-Specific Motion Analysis Understanding the sport-specific movements that trigger symptoms is crucial. This helps in correlating the athlete’s pain with their specific athletic activities.
- Physical Examination A combination of physical examination tests can enhance diagnostic accuracy. Tests such as the Neer test, Hawkins-Kennedy test, and the Jobe’s test can provide insights into the presence of impingement.
- Radiographic Evaluation Radiographic imaging, including X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is recommended to assess the extent of soft tissue abnormalities and structural damage. MRI is particularly useful in evaluating the rotator cuff tendons and the glenoid labrum.
Management Strategies
The management of shoulder impingement syndrome can be categorized into conservative and operative approaches, depending on the severity and chronicity of the symptoms:
- Conservative Management
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms is essential.
- Rehabilitation: A structured rehab program focusing on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles, improving scapular stability, and enhancing shoulder flexibility can be highly effective.

- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be used to manage pain and inflammation.
- Operative Management
- Arthroscopic Surgery: In cases where conservative treatment fails, arthroscopic surgery may be considered. This may involve decompression of the subacromial space, repair of rotator cuff tears, or addressing any structural abnormalities contributing to impingement.
Conclusion
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management, particularly for athletes engaged in overhead sports. By understanding the different types of impingement, utilizing a thorough diagnostic approach, and applying appropriate management strategies, athletes can effectively address shoulder impingement and return to their sport with reduced pain and improved function.
Whether you’re a healthcare professional or an athlete
experiencing shoulder issues, feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns, or staying informed about the latest developments in the management of shoulder impingement syndrome is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further complications.
Tweet