Total Knee Replacement
Posted on April 3rd, 2023 by Andries Lodder
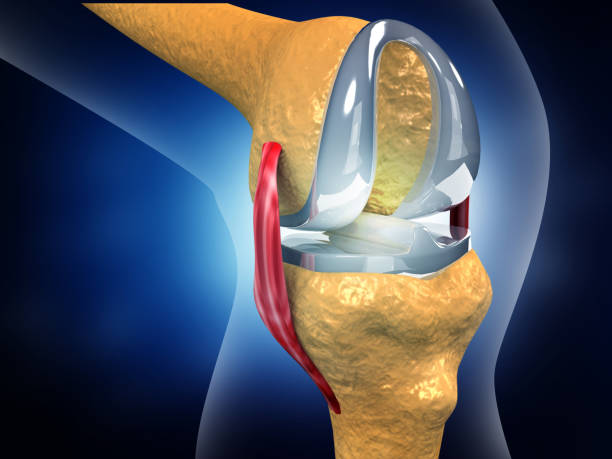
What is a total knee replacement?
A knee replacement, correctly termed knee arthroplasty, could be described as knee “resurfacing” as it is the surface of the bones that are being replaced. The damaged bone in the knee joint is removed and replaced with metal implants. A plastic spacer is placed in between the implants and the patella may be resurfaced as well at the surgeon’s discretion.
When is a knee replacement necessary?
If a knee replacement is suspected to be necessary, your doctor may refer you to an orthopaedic surgeon for a thorough evaluation to determine if you might benefit from this surgery.
Reasons surgery may be recommended:
- Severe knee pain or stiffness that limits everyday activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs.
- Moderate or severe knee pain while resting, either day or night.
- Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that does not improve with rest or medication.
- Knee deformity — a bowing in or out of the knee.
- Failure to substantially improve with other treatments such as anti-inflammatory medication, cortisone injections, lubricating injections, physical therapy, or other surgeries.
There are no absolute age or weight restrictions for total knee replacement surgery. Total knee replacements have been performed successfully at all ages, from young teenagers with juvenile arthritis to elderly patients with degenerative arthritis.
Recovery
Feeling some pain after surgery is normal as this is a natural part of the healing process. Your doctor and physiotherapist will work to reduce your pain, which can help you recover from surgery faster. Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery.
Foot and ankle movement is also encouraged immediately following surgery to increase blood flow in your leg muscles to help prevent leg swelling and blood clots.
Rehabilitation and Exercise
Most patients can begin exercising their knee soon after surgery. Specific exercises to strengthen your leg and restore knee movement will be given to allow walking and other normal daily activities soon after your surgery. The success of your surgery will depend largely on how well you follow your orthopaedic surgeon’s instructions at home during the first few weeks after surgery.
Exercise is a critical component of home care, particularly during the first few weeks after surgery. Through following carefully constructed programs, specific to you, you should be able to resume most normal activities of daily living within 3 to 6 weeks following surgery.
Your activity program should include:
- A graduated walking program, initially in your home and later outside, to slowly increase your mobility.
- Resuming ordinary household activities, such as sitting, standing, and climbing stairs.
- Specific exercises several times a day to restore movement and strengthen your knee.
Tweet