Lower Back Pain
Posted on March 12th, 2019 by Andries Lodder
Over 80% of all adults will experience lower back pain at some point in their lives. Lower back pain is one of the leading causes of disability in the work place as well the top reasons for days of work missed. It can affect both men and women and can range from a constant dull ache to an intense sharp shooting pain. As it is so prevalent within the population it is fortunate that there are ways to prevent lower back pain from occurring. If these prevention’s fail then simple treatment plans and the correction of body biomechanics can often relieve the back pain before it becomes debilitating.
Pathophysiology
There are numerous causes of lower back pain. These causes can range from; improper lifting technique, poor posture, age related spine and joint changes, accidents, poor exercise form and leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Lower back pain can be acute, lasting for a few days or weeks or chronic which is long term and can lasts for months and years. The majority of acute lower back pain cases are mechanical in nature. This means there is a disruption to one of the components of the spine, muscles, inter vertebral discs or nerves. Roughly 20% of individuals that experience an acute episode of lower back pain develop chronic pain.
Anatomy
The back is made up of a variety of structures. It has 33 irregular bones called vertebrae. Between each vertebra there is an inter-vertebral disc (IVD). These discs act as cushions and absorb the shock up the spine.
Each disc has a similar construction to a car tyre. An outer ring which is made up of fibrous bands is called the Annulus. The inside of this band is filled with a gel like substance called the Nucleus Pulposus. The discs act like coiled springs, with the Annulus pulling the vertebrae together against the elastic resistance of the nucleus on the inside.
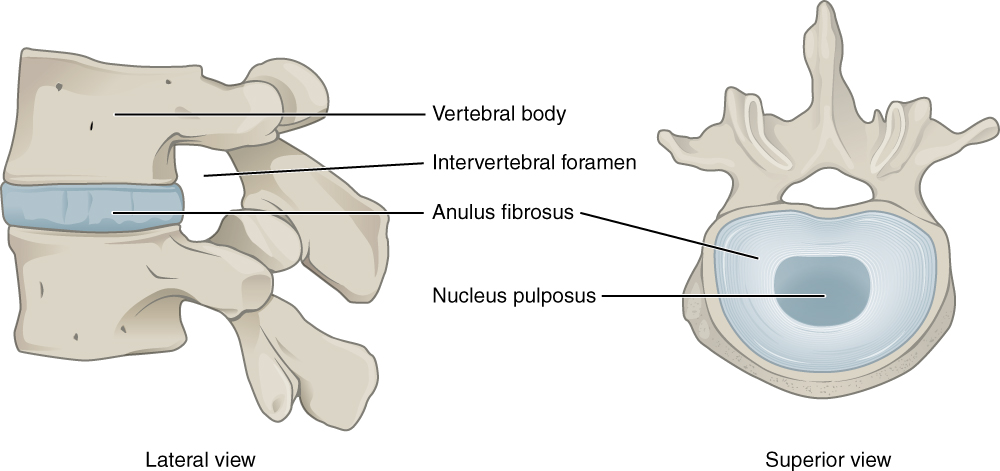
Bands of tissue known as ligaments hold the vertebrae in place, and tendons attach the muscles to the spinal column. Thirty-one pairs of nerves are rooted to the spinal cord and they control body movements and transmit signals from the body to the brain.
The lower back supports the weight of the entire upper body. The muscles of the lower back are primarily responsible for the flexing and rotating of the hips while walking and performing everyday movements. They also assist in the support of the spinal column.
The majority of lower back pain is as a result of injury to either the muscles, ligament, joints or discs within the back. Various causes of lower back pain affect different structures.
Causes
- Muscle Strain or ligament Sprain:
- Repeated heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement can strain the back muscles and spinal ligaments. If you’re in poor physical condition, constant strain on your back can cause painful muscle spasms.
- Bulging or Ruptured Disks:
- The soft material inside an inter-vertebral disk can bulge or rupture and press on a nerve. However, you can have a bulging or ruptured disk without back pain.
- Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back. In some cases, arthritis in the spine can lead to a narrowing of the space around the spinal cord, a condition called spinal stenosis.
- Skeletal irregularities:
- A condition in which your spine curves to the side (scoliosis) also can lead to back pain.
- Osteoporosis:
- The spine’s vertebrae can develop compression fractures if your bones become porous and brittle.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms can be varied. They can also begin suddenly or over a period of time.
Identifying the specific signs and symptoms can help identify the exact cause of the lower back pain and therefore assist in the treatment of the problem.
The signs and symptoms can include:
- Muscles spasms and aches
- Shooting or stabbing pains
- Radiating pain down one or both legs
- Pain when bending, lifting or twisting
- Pain that worsens after prolonged sitting or standing
Diagnosis
The most important aspect of lower back pain is the diagnosis. As there are multiple causes of lower back pain this is the most important area to identify. Without the underlying cause of the pain, the problem cannot be treated.
Various health care professionals such as a physiotherapist and biokineticists can perform a variety of assessments and special tests to identify basic causes of lower back pain.
If the pain is more serious then tests such as X rays and MRI’s are required to identify the underlying cause of the back pain. In these cases the back pain is usually structural and cause by bone, ligament of disc.
Treatment
As there are multiple causes of lower back pain and so there is not one treatment that will work for everyone. However, there are a few simple treatment options you can try.
One of the most important areas to look at when treating lower back pain is how long an individual remains seated for. Simply put movement is essential in treating lower back pain and remaining seated for extended periods of time is detrimental.
When treating lower back pain a multi-disciplinary approach is beast. Physiotherapists, Chiropractors, Doctors and Biokineticists can all provide essential input when dealing with lower back pain and assist in its prevention and treatment. Physiotherapists and Chiropractors can assist with the necessary joint mobilization and soft tissue release. Biokineticists can assist with strengthening exercises and stretches. While in more serious cases the input from a Doctor or Surgeon will be necessary.
Exercises:
One of the primary treatments for Lower back pain is using exercise to strengthen the core and stabilizer muscles and stretches to stretch those muscles that are tight and causing pressure to be placed on the lower back.
Trunk Rotations:
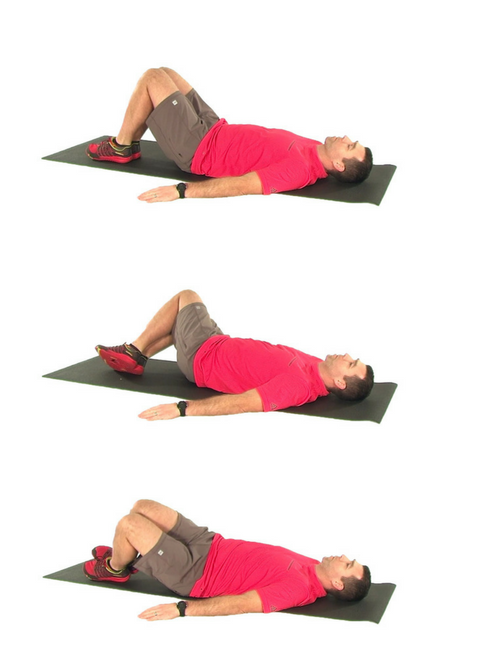

- Lying on your back with your hands at your sides and knees bent
- Keeping the feet flat on the floor, roll the knees from side to side
- Make sure to keep both shoulders and hands flat on the floor
- This exercise can also be done with the feet up on a Swiss Ball if one if available
- Perform 3 sets of 20 rolls
Should the symptoms of lower back pain persist for longer than 3 months with no relief after trying various treatment methods, it is advised to seek the help of a medical doctor who can advise if an x ray or MRI is necessary to determine if there is a more serious cause behind the pain.
If you are suffering from lower back pain the best thing to do is to go for an assessment. This way the underlying cause of your back pain can be identified and the treatment can be more specific and effective.
Contact us today to book yours.
Tweet