Performance Enhancement Training Part 4 – Plyometric Training
Posted on October 31st, 2016 by Andries Lodder
PLYOMETRIC TRAINING
So far we have discussed the first 3 parts of performance enhancement training.
- First we covered the importance of sport specific training and how to achieve equilibrium through integration for optimal performance.
- Then we got to the second part where we emphasized the importance of core stability and how it assists in injury prevention and forms the foundation for improved performance.
- Thirdly we discussed the role of eccentric training and how slowing down a specific movement during your training can actually increase your strength, improve stability and how that absorbed energy can be used as an elastic recoil to perform the next movement more explosively.
- This leads us into the fourth and final part, a Plyometric movement, which will only be performed when we have strengthened your ligaments and tendons, so that it can handle the forces of a ballistic movement without injuring yourself.
So, what is a Plyometric Training?
Let’s look at the basis of a Plyometric Movement
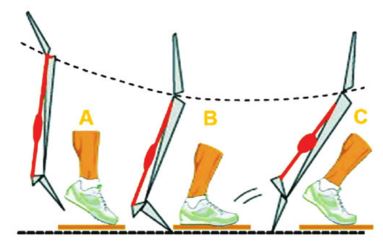
Currently, typical Plyometric Training comprises three phases (Illustration above). The first phase (A) is a rapid muscle lengthening movement known as the eccentric phase, therefore the preactivation phase. The second phase (B) involves a short resting period known as the amortization phase, this is where elastic energy is stored and muscle spindles are stimulated, and, in the third phase (C), the athlete engages in an explosive muscle shortening movement, termed the concentric phase, where all the stored elastic energy is released. The athlete repeats this three-part cycle as rapidly as possible, with the goal being to decrease the amount of time in between the eccentric and concentric movements. Reductions of time in between eccentric and concentric movement induce the athlete to become faster and more powerful as this primarily improves muscular, tendon and nerve functions.
Importance for Ultimate Performance
The increase in physical power make athletes run faster, jump higher and hit harder and develop specific skills such as injury protections relative to specific practiced sport. In addition, the forces involved and the quickness of execution induced the involvement of the central nervous system. Plyometric training has shown improvements include muscular and tendon strengthening and resulting in the ability to avoid injuries.
Thus, to get the competitive edge over your rivals and improve your physical conditioning to a different level, Plyometric Training must form a part in all athletic training programmes, in all types of sports. There are many safety consideration to be taken into account, including, evaluation of the athlete, ensuring facilities and equipment are safe, establishing sport-specific goals, determining programme design variables. Teaching the athlete proper technique and properly promoting the programme are by far the most important part before commencing in any Plyometric program.
We have come to the end of the 4 Parts for performance enhancement training. It has been a pleasure to share with you my thoughts and believes on this topic. If you feel like your current conditioning programme doesn’t live up to your expectations and needs, please contact me and I will do my best to help you reach your goals!
Tweet